Prokaryotes Produce the Majority of Their Atp
Select the two mechanisms that eukaryotic cells and aerobic prokaryotic cells combine to synthesize the majority of their ATP. Prokaryotes such as anaerobic bacteria rely heavily on the first stages of glucose break down - deriving enough energy from the breaking and restructuring of chemical bonds to make 2 ATPs per glucose.
How Much Atp Is Produced In A Prokaryotic Cell In A Krebs Cycle And Etc Quora
Prokaryotes lack mitochondria and instead produce their ATP on their cell surface membrane.
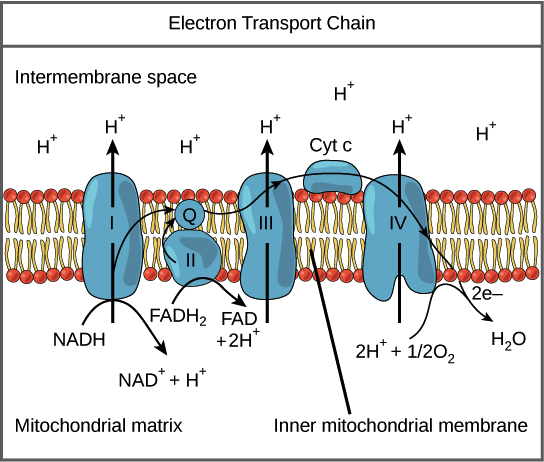
. Plastids are found in photosynthetic protists and plants chloroplasts are one type of plastid plastids can be a site of synthesis and storage of food reserves plastids often contain pigments. In prokaryotes there are no mitochondria the whole process of respiration occurs within the cytoplasm so no ATP is consumed in transporting across the organelle. Therefore 38 ATPs are made from one glucose in bacteria while 36 are made in a eukaryotic cell.
See full answer below. ATP is generated in the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells. It is an organic molecule.
ATP is the main energy storage molecule found in cells. Why do prokaryotic cells produce more ATP than eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria for example are organelles that provide eukaryotes with most of their energy by producing energy-rich molecules called ATP.
Start studying Microbiology Chapter 5. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Describe the process of energy transfer from NADH and FADH to the proton motive force.
Each organelle supports different activities in the cell. Prokaryotes lack mitochondria and instead produce their ATP on their cell surface membrane. Describe the process of energy transfer from the proton motive force to ATP.
ADP Pi ATP Eukaryotes and aerobic prokaryotes produce the vast majority of. Every time a eukaryotic cell divides to produce two new daughter cells all the DNA molecules of the parent cell are faithfully copied and combined with histones to form compact packages. Select the 2 mechanisms that eukaryotic cells and aerobic prokaryotic cells combine to synthesize the majority of their ATP - substrate level phosphorylation - oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxidative phosphorylation Substrate-level phosphorylation. What powerhouse organelle produces the majority of ATP in most eukaryotic cells. What is produced in eukaryotic cells.
ATP synthase uses the energy from the proton gradient to catalyze the reaction. These electrons with their energy depleted are then donated to oxygen hence the term oxidative phosphorylation. We know that oxidative phosphorylation produces the majority of ATP in eukaryotic cell respiration.
Mitochondria and chloroplasts can produce more ATP per glucose molecule however both rely on the presence of oxygen to keep the flow of energy moving. Be sure to include how free energy is changing and what the sources of energy are in.

Electron Transport Chain An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora

Atpase Supported Mitoflash Biogenesis A Experimental Design Atp 3 Download Scientific Diagram
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
4 3 Citric Acid Cycle And Oxidative Phosphorylation Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
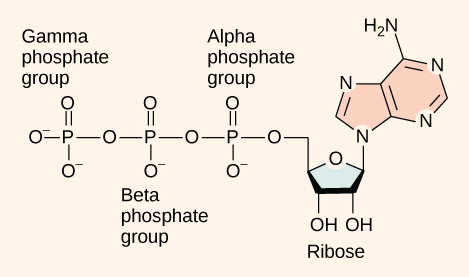
Atp Adenosine Triphosphate Biology 2e
What Process Produces Most Atp In Eukaryote Cells Quora
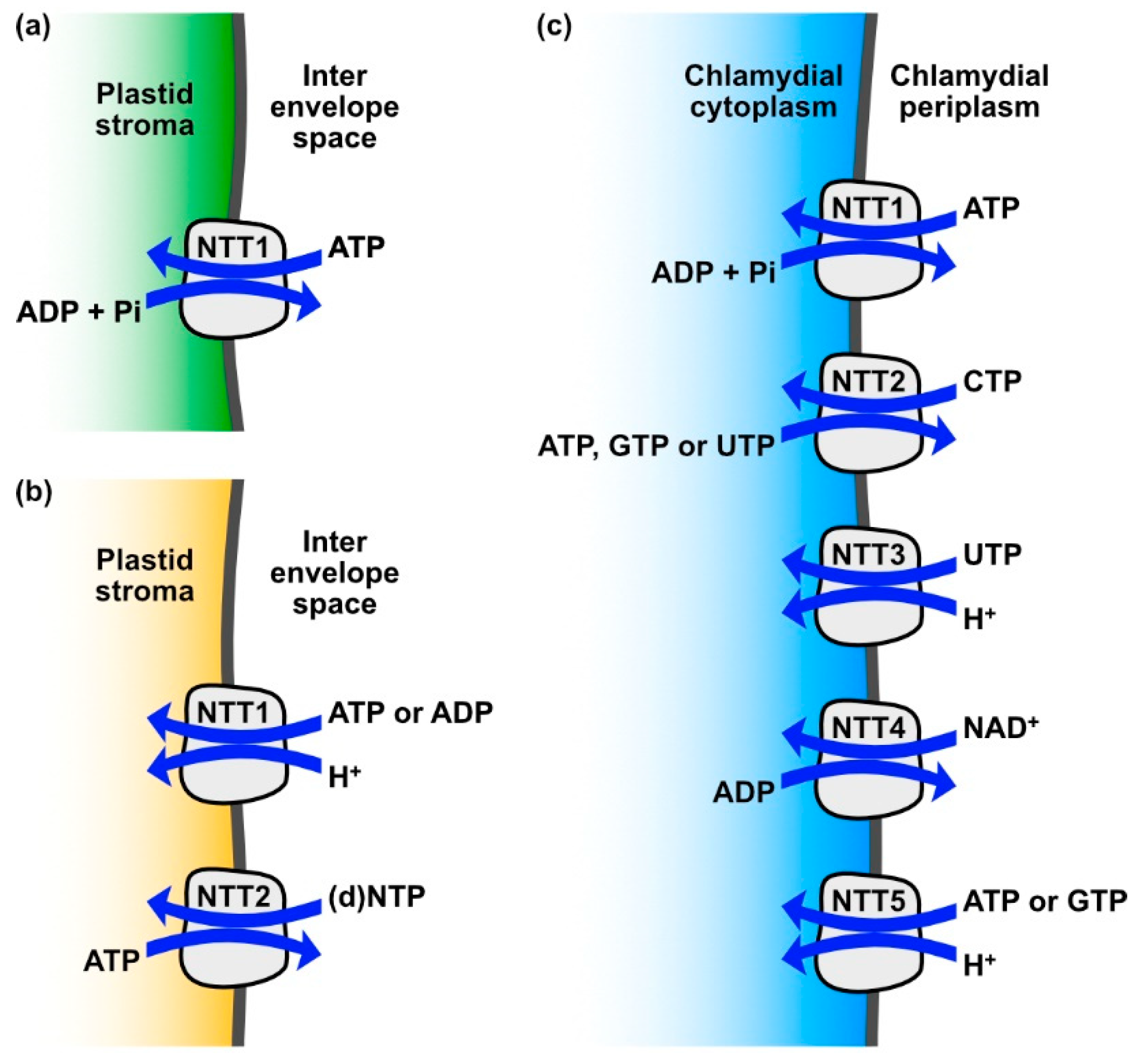
Biomolecules Free Full Text Nucleotide Transport And Metabolism In Diatoms Html

Cellular Respiration Microbiology

Pentose Phosphate Pathways Pathway Ii Biochemistry Notes Biochemistry Science Biology

Details Of The 10 Steps Of Glycolysis Part 2 Of 2 Chemistry Education Biochemistry Biochemistry Notes
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
How Do Prokaryotes Produce Atp Without Mitochondria Quora
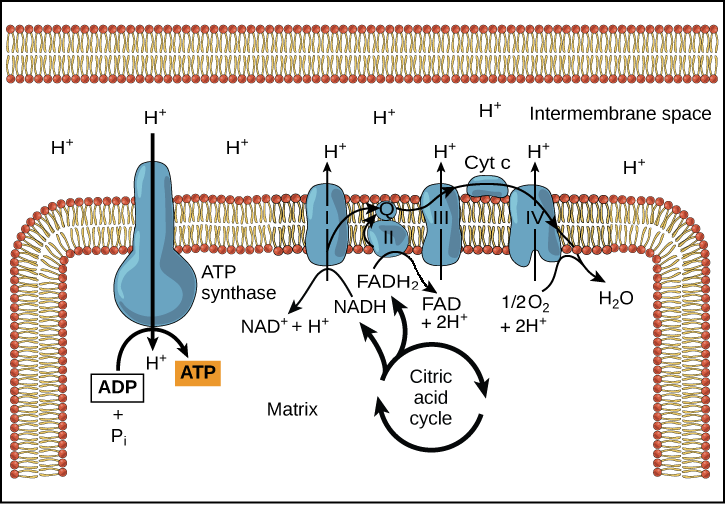
Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Article Khan Academy
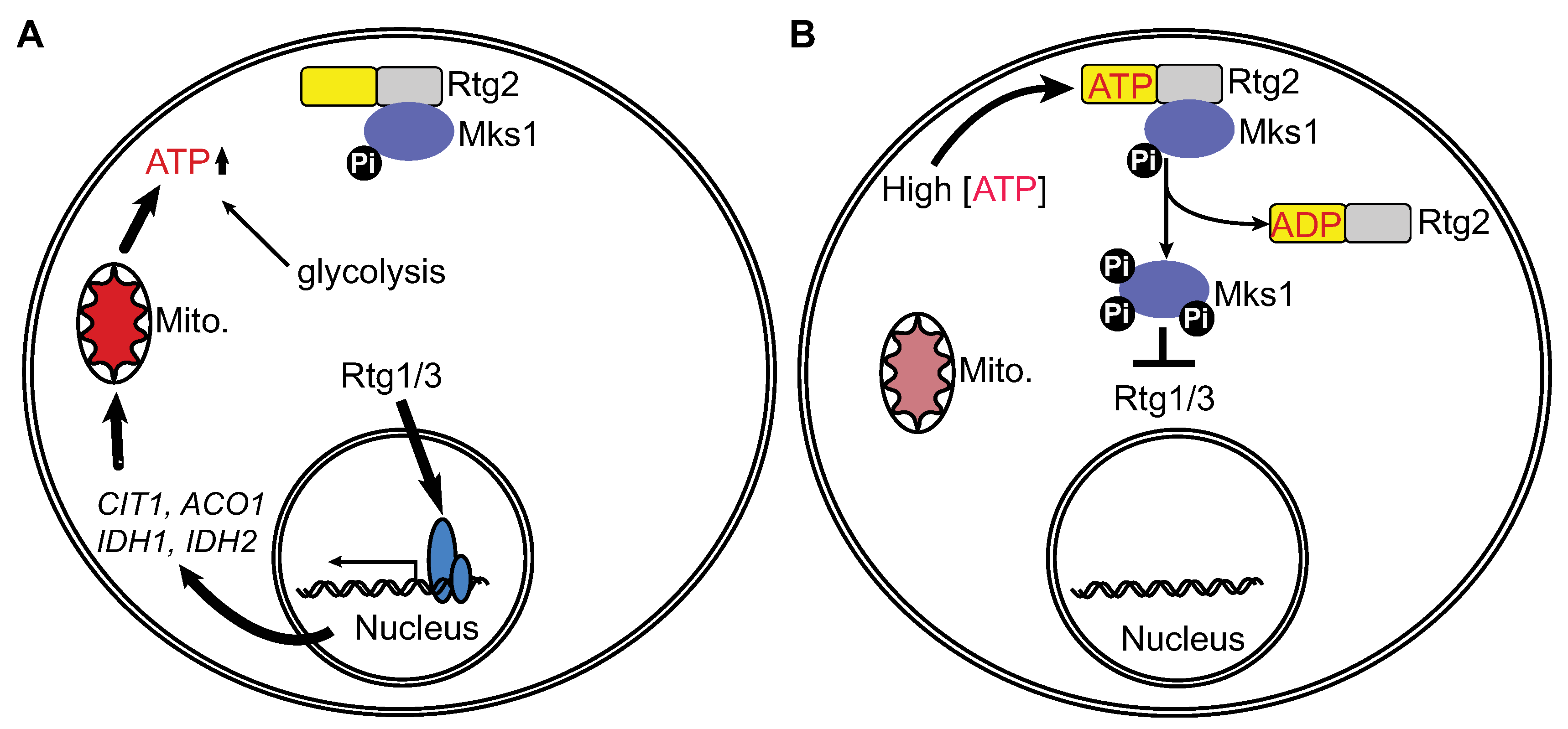
Genes Free Full Text Adenosine Triphosphate Atp Is A Candidate Signaling Molecule In The Mitochondria To Nucleus Retrograde Response Pathway Html

Comments
Post a Comment